Prof. Siegfried Seinecke with a veena

- Photographs , Faculty, Music
This section will be updated soon.
Chairman A. M. M. Arunachalam and others, IIT Madras

- Photographs , Administrators
This section will be updated soon.
Prof. Siegfried Seinecke at the Bose-Einstein Guest House

- Photographs , Faculty, Campus Facilities
This section will be updated soon.
A photograph of students in the Central Library

- Photographs , Academic Facilities, Campus Facilities
This section will be updated soon.
Natural fibres used at the FRP Centre
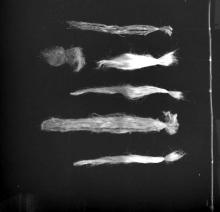
- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
Natural Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites or NFPCs are mostly used in non-load bearing indoor components in civil engineering because of their vulnerability to environmental attack. Some of the natural fibres used in the manufacturing of NFPCs are sisal, coir, oil palm, jute, pineapple, hemp and bamboo. The fibres seen in the image are possibly coir pith. IIT Madras set up six centres in the year 1973. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre, was one of them. The centre was officially opened in March 1974 and its key…
A Hydraulic Press at the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
Seen in the image is a 150 tons Hydraulic Press that was used for press moulding studies. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre was started at IIT Madras in March 1974. It was started due to the increased use of FRP, on a global scale, for advanced technology applications as well as for commercial and domestic applications. Prior to the formation of the Centre, in 1960, research and development activities in this area was initiated by the Department of Aeronautical Engineering (IIT Madras) because of the possible and…
Natural fibres used at the FRP Centre
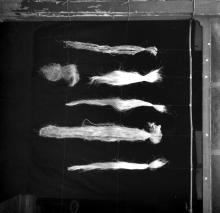
- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
Natural Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites or NFPCs are mostly used in non-load bearing indoor components in civil engineering because of their vulnerability to environmental attack. Some of the natural fibres used in the manufacturing of NFPCs are sisal, coir, oil palm, jute, pineapple, hemp and bamboo. The fibres seen in the image are possibly coir pith. IIT Madras set up six centres in the year 1973. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre, was one of them. The centre was officially opened in March 1974 and its key…
Coir pith products (with FRP skin) made at the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
Seen in the image are coir pith tables with FRP skins. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre was started at IIT Madras in March 1974. It was started due to the increased use of FRP, on a global scale, for advanced technology applications as well as for commercial and domestic applications. Prior to the formation of the Centre, in 1960, research and development activities in this area was initiated by the Department of Aeronautical Engineering (IIT Madras) because of the possible and increasing applications of FRP in the…
Natural fibres used at the FRP Centre
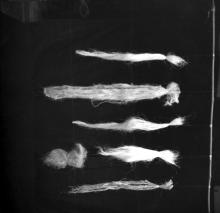
- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites or NFPCs are mostly used in non load bearing indoor components in civil engineering because of their vulnerability to environmental attack. Some of the natural fibers used in the manufacturing of NFPCs are sisal, coir, oil palm, jute, pineapple, hemp and bamboo. The fibres seen in the image are possibly coir pith. IIT Madras set up six centres in the year 1973. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre, was one of them. The centre was officially opened in March 1974 and its key…
Sheet moulded components made at the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
The sheet moulded components seen in the image are made from sheet moulding compounds (SMCs). SMCs are ready to mould glass-fibre reinforced polyester material primarily used in compression moulding. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre was started at IIT Madras in March 1974. It was started due to the increased use of FRP, on a global scale, for advanced technology applications as well as for commercial and domestic applications. Prior to the formation of the Centre, in 1960, research and development activities in this…
Sub-assembly (outside view) of the geodesic dome that was designed by the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
In 1970, when R. Buckminster Fuller received a gold-medal for his development of the geodesic dome, the American Institute of Architects called it “the strongest, lightest and most efficient means of enclosing space yet known to man.” The spherical form of the dome is composed of triangular facets, which can withstand pressure on all sides. Fuller discovered that a sphere created with triangles could have unparalleled strength. The geodesic dome (15 meters diameter) seen in image 0295 of this album was made out of pentagonal panels as seen in this photograph. Each panel was assembled using…
Sub-assembly (outside view) of the geodesic dome that was designed by the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
In 1970, when R. Buckminster Fuller received a gold-medal for his development of the geodesic dome, the American Institute of Architects called it “the strongest, lightest and most efficient means of enclosing space yet known to man.” The spherical form of the dome is composed of triangular facets, which can withstand pressure on all sides. Fuller discovered that a sphere created with triangles could have unparalleled strength. The geodesic dome (15 meters diameter) seen in image 0295 of this album was made out of pentagonal panels as seen in this photograph. Each panel was assembled using…
Sub-assembly (outside view) of the geodesic dome that was designed by the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
In 1970, when R. Buckminster Fuller received a gold-medal for his development of the geodesic dome, the American Institute of Architects called it “the strongest, lightest and most efficient means of enclosing space yet known to man.” The spherical form of the dome is composed of triangular facets, which can withstand pressure on all sides. Fuller discovered that a sphere created with triangles could have unparalleled strength. The geodesic dome (15 meters diameter) seen in image 0295 of this album was made out of pentagonal panels as seen in this photograph. Each panel was assembled using…
Coir pith products (with FRP skin) made at the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
Seen in the image are coir pith tables with FRP skins. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre was started at IIT Madras in March 1974. It was started due to the increased use of FRP, on a global scale, for advanced technology applications as well as for commercial and domestic applications. Prior to the formation of the Centre, in 1960, research and development activities in this area was initiated by the Department of Aeronautical Engineering (IIT Madras) because of the possible and increasing applications of FRP in the…
A filament wound FRP tube that was made at the FRP Centre

- Photographs , Equipment , 1970s
Filament winding is a process of manufacturing when individual filaments are run through a resin bath and wound onto a mandrel. Some of the products made using this technique of manufacturing are golf club shafts, automobile drive shafts, sailboat masts, oars and paddles for small boats, small aircraft fuselages, spacecraft structures and pressure vessels like fire-fighter oxygen bottles. The Composite Structures (FRP) Research Centre, also known as the Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) Centre was started at IIT Madras in March 1974. It was started due to the increased use of FRP, on a…
- Contribute
to the Centre -
Monetary
Support - Digital
Material









